Deployment Automation
Modular Deployments
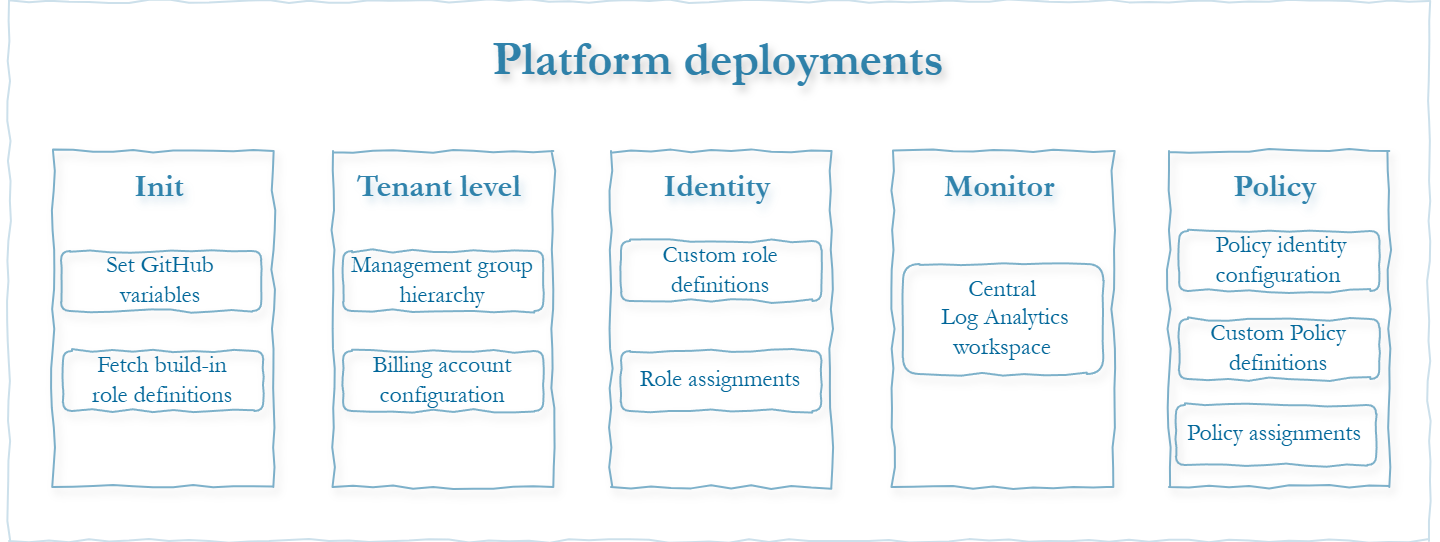
Deployments are designed with modular components, grouping Azure services by their specific capabilities. Each module focuses on a distinct area—such as monitoring, identity, or policies—ensuring that all resources and configurations for that capability are deployed together. This clear separation avoids overlaps, defines boundaries, and allows engineers to work independently.
This method brings several advantages.
- Parallel Development: engineers can work on separate modules simultaneously without conflicts or overwriting changes.
- Scalability: adding new features or expanding existing ones becomes simple and efficient.
- Simplified Maintenance: updates and troubleshooting are more manageable since each module operates independently
Bicep templates are the backbone of this approach. Each deployment workflow uses task-specific Bicep templates that prioritize clarity and adaptability over reusability. This keeps them easy to read, adjust, and align with the lightweight, modular philosophy
Azure Deployment Stack
The Deployment Stack in Gazelle provides management of the Azure resource lifecycle, from deployment to deletion. Resources defined in Bicep templates are provisioned in Azure, and any resources no longer defined in the templates are seamlessly removed. This approach ensures that templates remain the single source of truth, reducing the need for manual clean-up tasks.
The Deployment Stack adds an extra layer of control with ‘deny settings’, which prevent write or delete actions on managed resources—even if a service principal has the necessary RBAC permissions. This safeguard ensures critical resources remain secure from accidental modifications or deletions.
This feature is particularly useful for platform-managed resources within application landing zones. It lets application teams perform predefined tasks while keeping these resources protected from unauthorized changes. The result is a balance that empowers teams to work efficiently while maintaining the stability of the landing zones
Test Environment
All platform changes are first deployed to a fully isolated test environment, designed as a complete replica of production. This environment includes its own identity, management group hierarchy, policy assignments, and all other Azure components, ensuring thorough testing without risking live systems. Isolation is achieved through practices such as:
- Main Branch Protection
- GitHub Environments
- Automated Workflows
- Eliminating direct human access
This approach ensures every change is tested before being promoted to production, keeping the platform stable and predictable.
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions are the engine behind Gazelle’s deployment automation, ensuring seamless operations across environments. Built for maintainability and scalability, these workflows are structured into two key parts: template workflows and deployment workflows
Template Workflows: focus on what needs to be deployed. They include the core deployment logic, handling everything from start to finish.
Deployment Workflows: define when and where templates are applied. They manage triggers, target environments, and deployment-specific parameters, executing the logic set by templates.
This clear separation keeps the platform lightweight, easy to maintain, and ready to scale as needs evolve.
Landing Zone Workflows
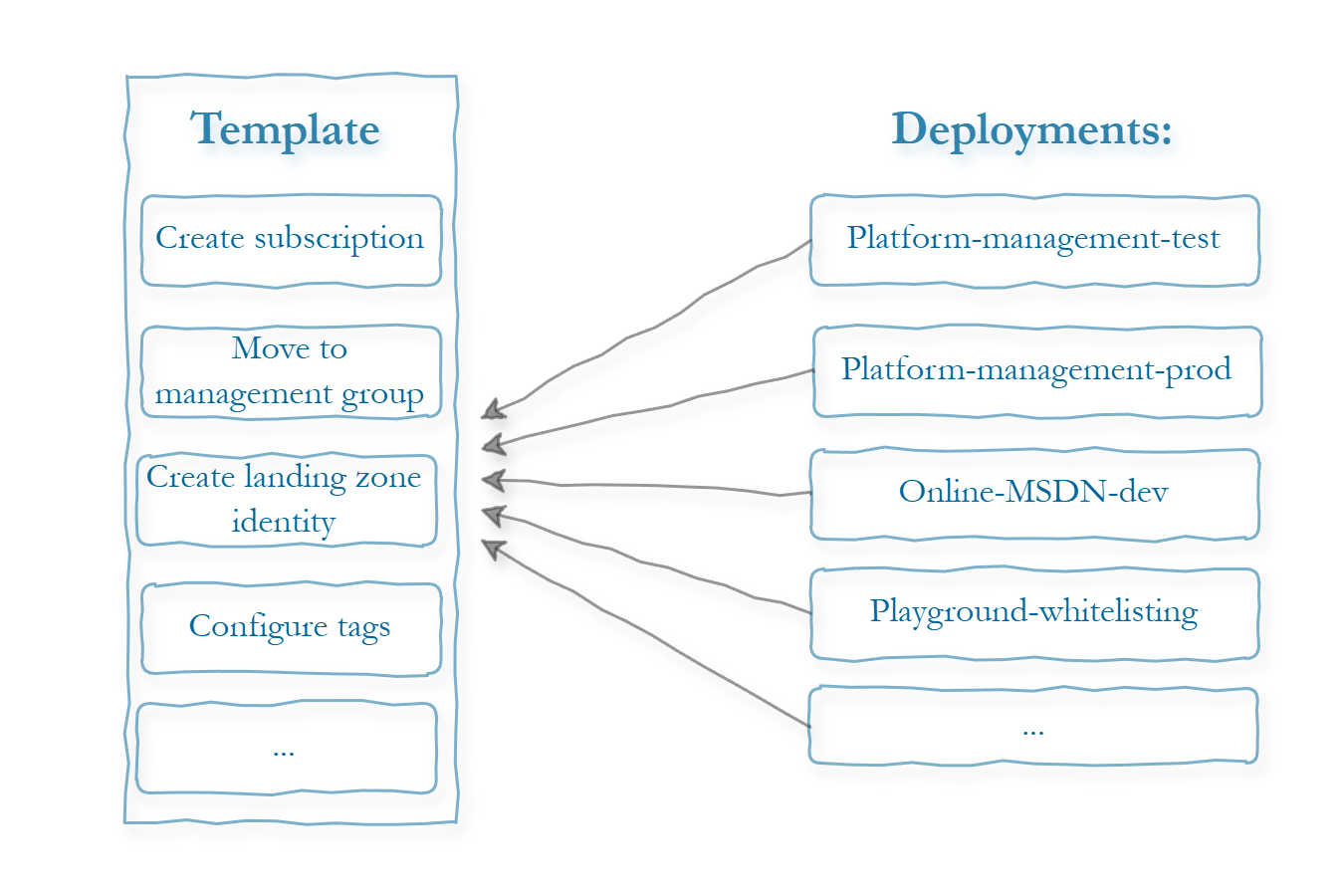
Landing zone workflows follow a 1-to-many relationship: a single template workflow serves as the foundation for all landing zone deployment workflows.
- During the landing zone setup process, deployment workflow is generated.
- Pipelines are triggered automatically whenever the landing zone parameters file is edited.
Platform Workflows
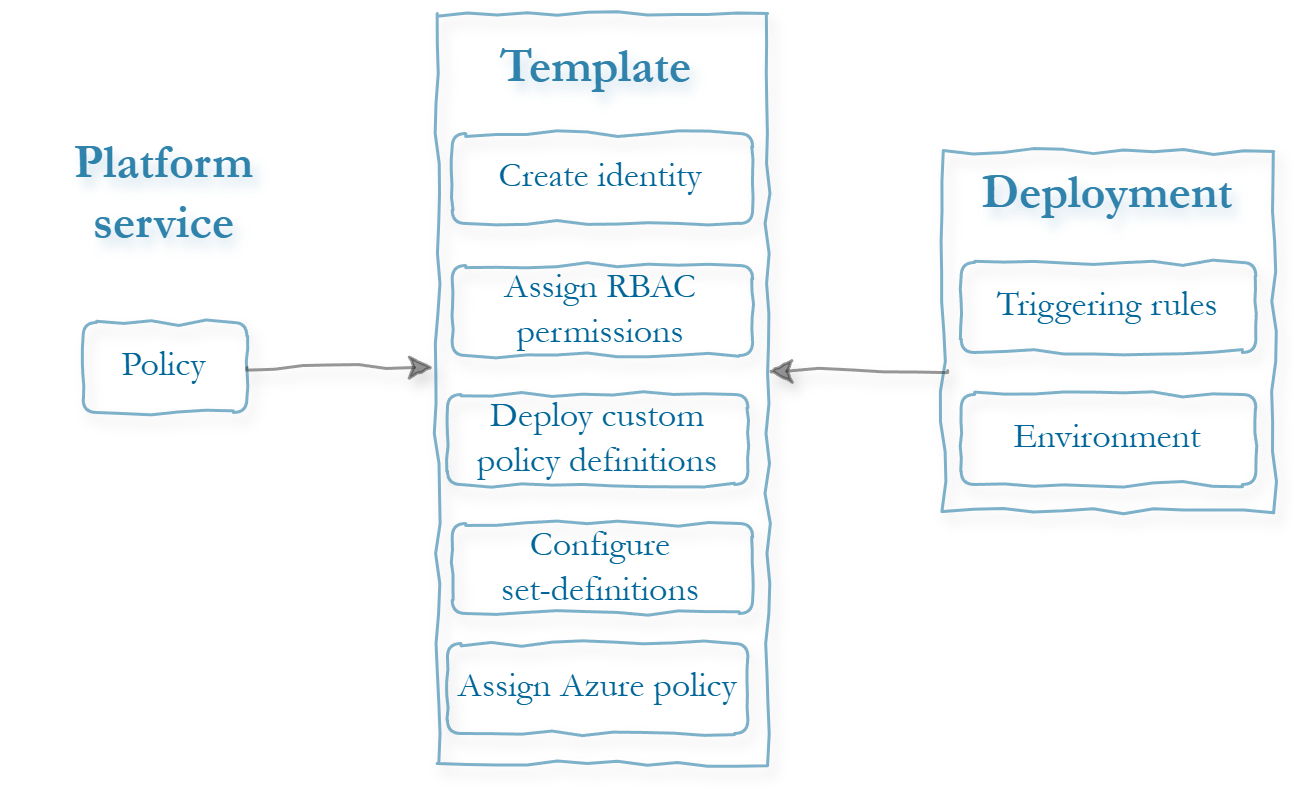
Platform workflows are grouped by Azure platform capabilities, as outlined in the Modular Deployment section. This approach follows a 1-to-1 mapping principle, where each Azure platform service is associated with a single template and its own dedicated deployment workflow.
- GitHub Actions are triggered automatically whenever any file associated with a workflow is changed.
BigBang
Unforeseen failures shouldn’t lead to downtime or complex recovery processes. The BigBang principle ensures that platform services can always be redeployed from scratch, providing a reliable fallback mechanism. By treating the platform as fully disposable and repeatable, BigBang simplifies recovery and guarantees operational continuity.
Destroy Azure Platform
The ‘Destroy Azure Platform’ pipeline provides a way to clean up the platform environment without affecting application landing zones. It removes resources tied to platform landing zones, deployment histories, management groups, and GitHub environment variables. After cleanup, the platform can be effortlessly restored to a fresh state by running the ‘BigBang’.